Stress in birds
25/01/2024Human dimensions in species conservation
Historically, species conservation has been a discipline dominated by natural scientists. Their knowledge has become the basis of species conservation through evaluating population fluctuations, identifying threats, and ultimately proposing conservation measures based on these observations and focused on addressing the needs of endangered species. Also historically, true integration of and sufficient emphasis on all the human dimensions of conservation has been underemphasized. Incorporating the human dimension in species conservation is important for several reasons. Firstly, local communities often live near wildlife habitats. Their participation is crucial; they have traditional knowledge of ecosystems and can provide invaluable insights into sustainable conservation practices.
It is also important to consider the needs and livelihoods of these communities. Conservation initiatives that respect and support the local economy and culture can reduce human-wildlife conflict. Sustainable development programs can provide alternative livelihoods, reduce pressure on natural resources and mitigate human-wildlife conflict. It is also important to understand the socio-economic factors that cause poaching, illegal wildlife trade and habitat destruction. Poverty, lack of education and limited opportunities often contribute to these activities. If these causes are addressed through education, job creation and community empowerment, the threat to wildlife can be significantly reduced.
In essence, including the human dimension in wildlife conservation is not just an option - it is a necessity. By respecting local communities, considering socio-economic factors, and recognizing our dependence on healthy ecosystems, we pave the way for more holistic and sustainable conservation measures that benefit both wildlife and people.
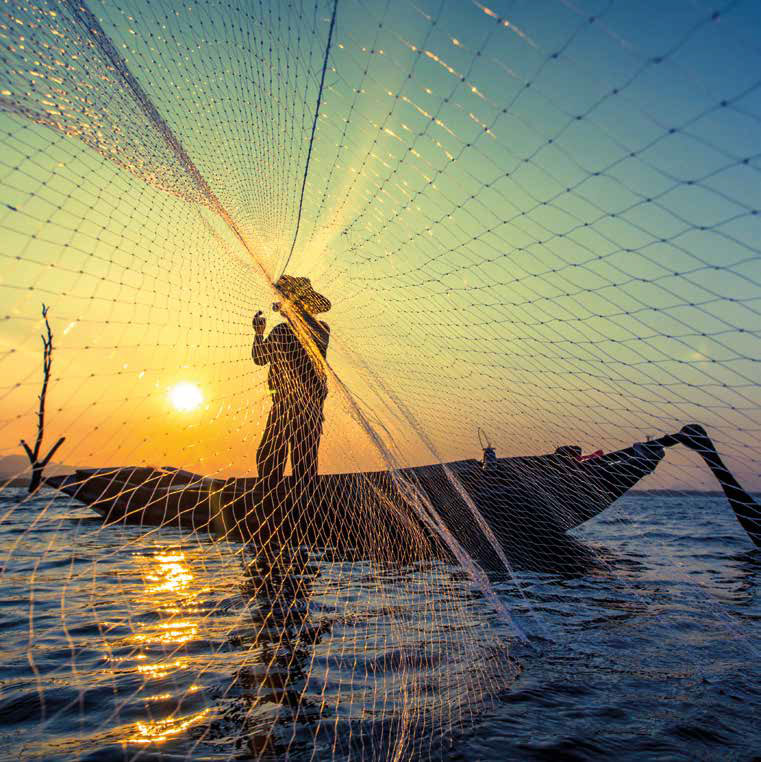

Our contribution
YAQU PACHA and Nuremberg Zoo have demonstrated a paradigm shift in wildlife conservation by emphasising the crucial role of local communities in their projects. Their approach embodies a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of people and wildlife, and forges partnerships with local people to conserve biodiversity. By actively involving and empowering these communities, YAQU PACHA has fostered a sense of stewardship among residents, using their traditional knowledge and cultural practices to inform conservation strategies. Their visionary approach also includes the dissemination of knowledge through scientific meetings that focus on the human dimension of conservation. By organizing international workshops, YAQU PACHA provides a platform for experts, researchers, and community leaders to share insights, best practices and innovative ideas focused on integrating human perspectives into conservation efforts. Their commitment to integrating the human dimension into conservation practices sets a precedent for inclusive and effective wildlife conservation worldwide.